This information HAS errors and is made available
WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY OF ANY KIND and without even the
implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. It is not permissible to be read by
anyone who has ever met a lawyer or attorney. Use is confined to
Engineers with more than 370 course hours of engineering.
If you see an error contact:
+1(785) 841 3089
inform@xtronics.com
EKG Stress tests and Nuk imaging don't tell you ANYTHING about the amount of plaque in your arteries other than they are not extremely blocked - and most heart attacks are not caused by nearly blocked arteries!
Look for a heart scan (not a CT angiogram) but a Coronary Calcium Scoring heart scan. You won't get an accurate score number for arteries that have stents - but even if you have one left, it can help you see if your intervention works. Once a year if you are tracking plaque..
These test are rightfully criticized as a tool to get people into the cath lab prematurely, but it is the only way you will know the health of your coronary arteries and CAD (Coronary Artery Disease) is a leading killer. Used as preventative medicine, they can help one tailor diet, vitamins and medicines to control the progress of CAD.
People with elevated lp(a) can have normal looking cholesterol tests and have aggressive CAD - There are ways to lower Lp(a) - I read one place that Lipitor can actually raise this level! You want this test in particle count (nmol/dl) not mass (mg/l) see NMR lp(a) test The mass test can vary 40% due to isoforms.
6 months
Lp(a) is really an LDL cholesterol particle bound to an additional protein called apoprotein(a) (apo(a)). LDL cholesterol particles, just like VLDL and IDL, each contain one apoprotein B molecule (apo B). The apo(a) particle binds to the LDL particle via apo B, and they do so through two linked sulfur molecules, the so-called “disulfide linkage.”
Sirtori CR, Calabresi L, Ferrara S, Pazzucconi F, Bondioli A, Baldassarre D, Birreci A, Koverech A. L-carnitine reduces plasma lipoprotein(a) levels in patients with hyper Lp(a). Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2000;10:247-251.
ApoA-I production is decreased by Vitamin D - Wehmeier K, Beers A, Haas MJ, Wong NC, Steinmeyer A, Zugel U, Mooradian AD (2005). "Inhibition of apolipoprotein AI gene expression by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1737
First, don't even look at your total cholesterol number, it fails to have much if any value. Basic Lipid targets of LDL 60 mg/dl, triglycerides 60 mg/dl or less, HDL 60 mg/dl or greater can be achieved. The problem here is that conventional lipid tests underestimate - often by 40-50% sometimes 100% the amount of LDL. There is a better NMR lipid test (You may have to find a lab that does not use labcorp which does not return all the numbers.) small vs large LDL - LDL-P Small-LDL-P (is this VLDL?) LDL-P is a very useful number that can be used to tweak treatment. This added detail is needed because not all LDL is terrible and not all HDLs are equally protective. The key number is not total LDL but the number of LDL particles. The standard test measures the wrong thing!
3 - 6 months
If you are stuck with only the 'standard' lipids tests and are eating low carb - consider the following link to correct the numbers:
Increasing HDL can be accomplished with cheap Niacin and D3 - more effective than any statin. HDL may help to slightly reverse arterial plaque. Or it might make things worse. NMR Lipid test cost $167 (2009)
Standard lipid tests can under report LDL by large amounts - besides the test measures the wrong thing - you really need to know particle counts to see if you are reaching targets.
The problem is current medicine is using the obsolete lipid tests - and trusting them can get you into big trouble. Finding a doctor that will order and use these tests is the big hurdle.
One time test - once you know it you can use the information to change interventions.
Full panel - some evidence that taking T4 + T3 is best for CAD.
Test 6-8 weeks till corrected - then every 6 months.
Other Free T3 reference ranges: TYP 350 - 420 pg/dL Some lab -- 140 – 420 pg/dL NACB consensus statement 200 – 500 pg/dL Family Practice Notebook 230 – 619 pg/dL Quest Diagnostics 230-420 pg/dL (BTW Quest uses a premier endocrinology laboratory, the Nichols Institute in San Juan Capistrano, CA, as their reference laboratory)
It is clear that the TYP range is tighter and centered higher.
According to Ken Woliner, M.D., A.B.F.P :
Hypothyroidism is associated with heart disease there may be something to treating with a combination T4 + T3 to help reduce Lp(a).
D3 can raise HDL (the good cholesterol) - some studies report reduction of CAD Target for D3 is either 50-60 ng/ml or 125-150 nmol/l (Others say 60-80 ng/ml is optimal)
Test 2-3 months until stable - then 6 months - February and August
No substitute for blood testing - response to supplements varies greatly.. Test every 3mo until stable - then once/ year.
You do NOT test via !>> 25(OH)D2 or 1.25(OH)2D <<!!
"GRAS [Global Risk Factor Assessment Score] was able to correctly differentiate a healthy person from a person with coronary artery disease 49% of the time, while oxLDL was correct 82% of the time. Thus, oxLDL by itself was far more accurate than a whole battery of traditional cholesterol and cardiac markers. Coronary patients had more than twice the level of circulating oxLDL than the healthy comparison group."'
That PUFA seems to increase Oxy-LDL is clear - but just like 'fats" PUFAs are not one thing - there are both O-6 and 0-3 PUFAs and several kinds of PUFAs I think it would be rather easy to clear this up. It seems that the tool of Oxidized LDL assays should help us optimize our diet strategy.
Once LDL accumulates in the subendothelial space, it tends to become modified or oxidized. This oxidized LDL plays several key roles in furthering the course of the inflammatory process. It is chemotactic to monocytes; oxidized LDL causes endothelial cells to secrete molecules that cause monocytes to penetrate between the endothelial cells and accumulate in the intima[6].
Oxidized LDL promotes death of endothelial cells by augmenting apoptosis. Also, through the activation of collagenases, ox-LDL contributes to a process which may lead to the rupture of the fibrous plaque Oxidized LDL decreases the availability of endothelial nitric oxide (NO), which, in turn, increases the adhesion of monocytes to the endothelium.
(Stress > homocysteine > plaque but may be indicator not cause?? Deplin L-Methylfolate?) It appears that B-vitamins lower homocysteine - but don't reduce CAD - side effect of high cortical levels? Methylfolate seems to CAUSE Restenosis according to this quality study (biggest shortcoming was it was only 60-month long)
There seems to be a lack of conclusion if lowering homocysteine with folate is of any benefit.
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and TMG also reduce homocysteine - they are all methyl donors - will they also induce Restenosis?
There are still some practical lessons to learn from homocysteine, even if you choose to not treat it: --It can indicate B12 and/or folate deficiency. B12 deficiency first detected by increased homocysteine is reasonably common. --There may be benefit in people with Lp(a), since homocysteine may enhance Lp(a) assembly --It can suggest or support the diagnosis of hypothyroidism. In fact, some have suggested that high homocysteine can be used as a surrogate for hypothyroidism. Beyond that, we sure need clarification on this question.
we could have the case that if homocysteine is high - slightly upping T4 may bring it down and might be a very useful treatment parameter?
One more reason we really need to be using computer 'expert systems' - homocysteine alone may not mean much - but combine it with somewhat elevated Lp(a) and/or subclinical hypothyroid results of TSH and Free T3 -- and the intervention becomes clear. I don't think the average doctor is going to see these patterns - we need to start using data mining now!
DHEA is precursive to several hormones. DHEA has also been shown to reduce the amount of atherosclerotic plaque in rabbits fed a high-cholesterol diet.
Not a specific cardiac marker, but can indicate systemic inflammation specific to the prostate in men
This is downstream of oxLDL and not as predictive.
Target less than 115/70
Phosphate levels are consistently linked with cardiac calcification
Creates chronic inflammation and other problems.
CRP is an inflammatory mediator released by the liver in response to IL-6(should we be tracking IL-6 instead). It prevents cholesterol from exiting macrophages in cell culture.
Inflammation is related to CAD
We want CRP to be below 1mg/l
Test quarterly
CRP may increase oxLDL levels
Correcting testosterone may lower oxLDL ""Castrated mice presented 1.7-fold higher titers of anti-oxidized LDL (Ox-LDL) antibodies than sham-operated controls.""
Causes the liver to make CRP
Might be able to lower this with Resveratrol.
Run a real glucose tolerance test
Buy a meter and some glucola
Fasting level every 3 months
It might be even more useful to see BG two hours after a meal - keep it below 110 via carb restrictions.
This pretty much tells us the average blood sugar over the last weeks or so.
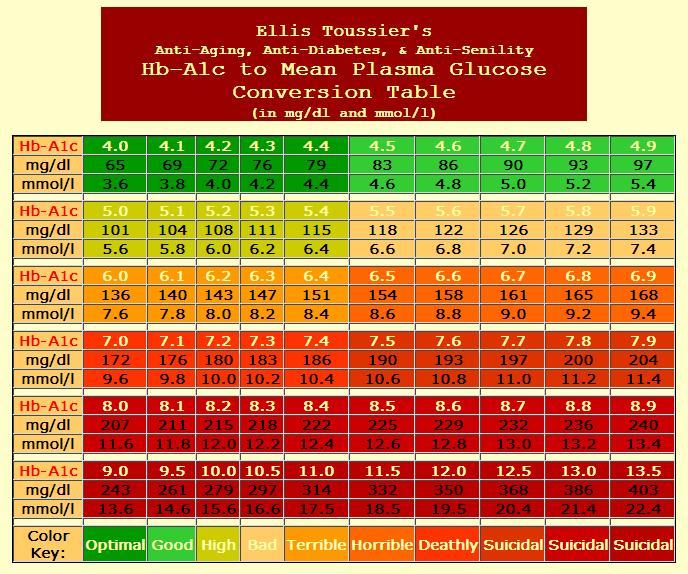
Convert A1C numbers to Blood Glucose Click to enlarge
Does not work as well as they say - low carbers can get false
numbers. Depends on turnover rate of red-blood-cells.
???
| Top Page | wiki Index |