This information HAS errors and is made available WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY OF ANY KIND and without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. It is not permissible to be read by anyone who has ever met a lawyer or attorney. Use is confined to Engineers with more than 370 course hours of engineering.
If you see an error contact:
+1(785) 841 3089
inform@xtronics.com
The electrical resistivity ρ (Rho (letter)) of a material is given by
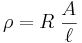
where
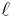 is the length of the piece of material (measured in meters, m);
is the length of the piece of material (measured in meters, m);
The standard is to measure in m2, but be warned that often you might need cm2 or sq mils.
| Material | Resistivity (Ω-m) at 20 °C | Coefficient* |
|---|---|---|
| Silver | 1.59×10-8 | .0038 |
| Copper | 1.72×10-8 | .0039 |
| Gold | 2.44×10-8 | .0034 |
| Aluminium | 2.82×10-8 | .0039 |
| Calcium | 3.3x10-8 | |
| Tungsten | 5.60×10-8 | .0045 |
| Nickel | 6.99×10-8 | ? |
| Iron | 1.0×10-7 | .005 |
| Tin | 1.09×10-7 | .0045 |
| Platinum | 1.1×10-7 | .00392 |
| Lead | 2.2×10-7 | .0039 |
| Manganin | 4.82×10-7 | .000002 |
| Constantan | 4.9×10-7 | .00001 |
| Lead | 2.2×10-7 | |
| Mercury | 9.8×10-7 | .0009 |
| Nichrome | 1.10×10-6 | .0004 |
| Carbon | 3.5×10-5 | -.0005 |
| Germanium | 4.6×10-1 | -.048 |
| Silicon | 6.40×102 | -.075 |
| Glass | 1010 to 1014 | ? |
| Hard rubber | approx. 1013 | ? |
| Sulfur | 1015 | ? |
| Paraffin | 1017 | ? |
| Quartz (fused) | 7.5×1017 | ? |
| PET | 1020 | ? |
| Teflon | 1022 to 1024 | ? |
| Top Page | wiki Index |
(C) Copyright 1994-2019
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.